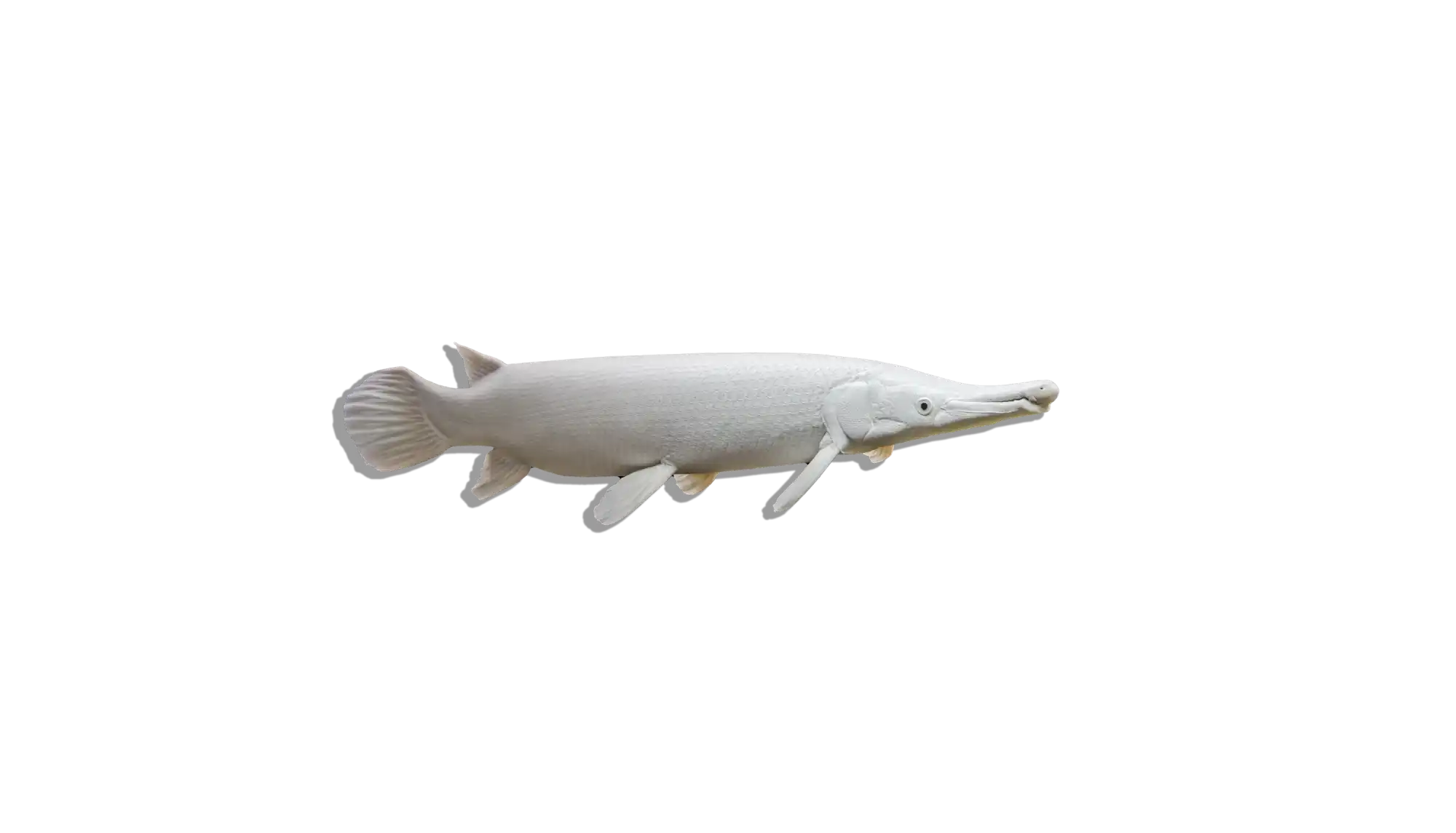
Description
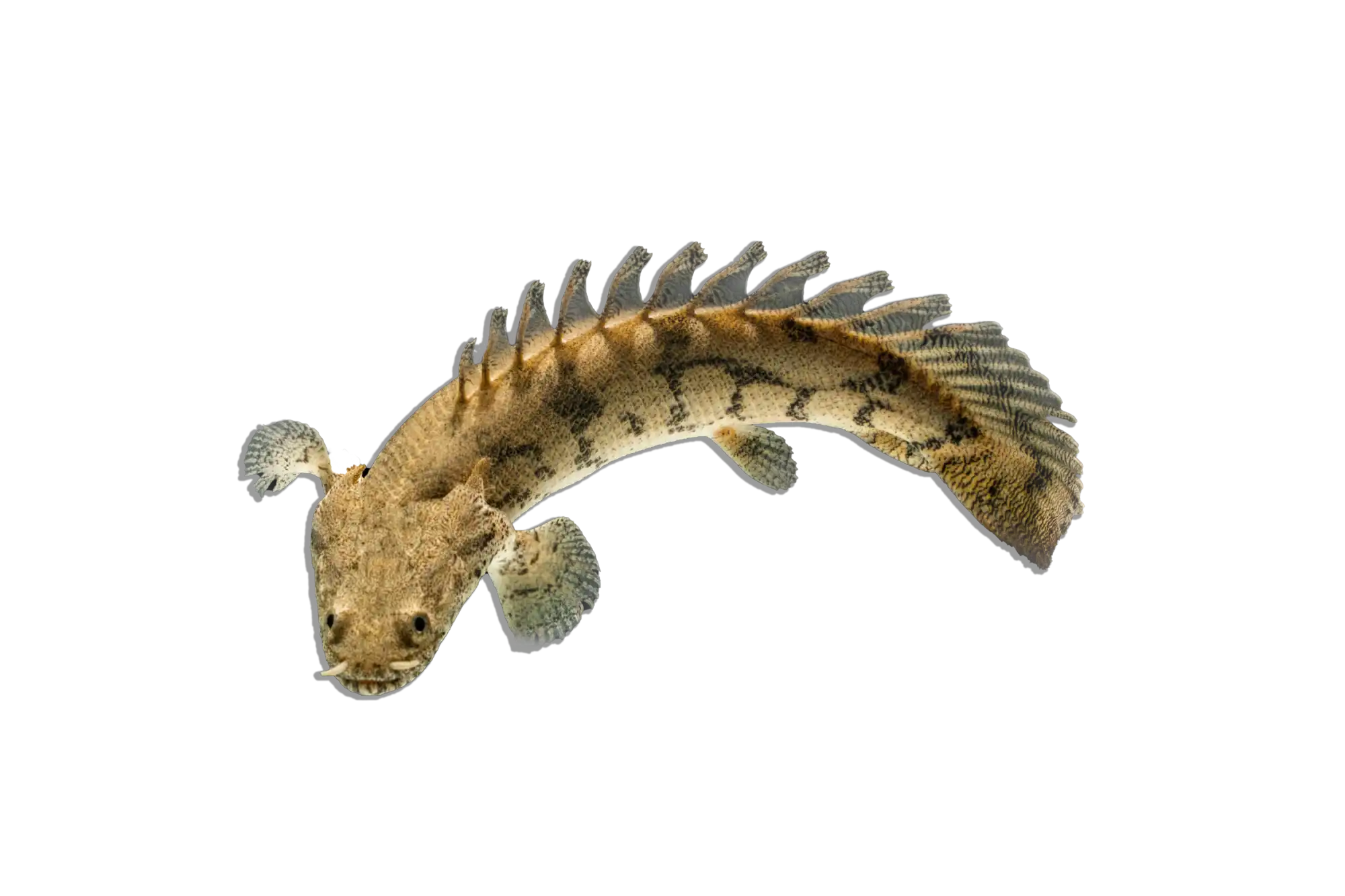
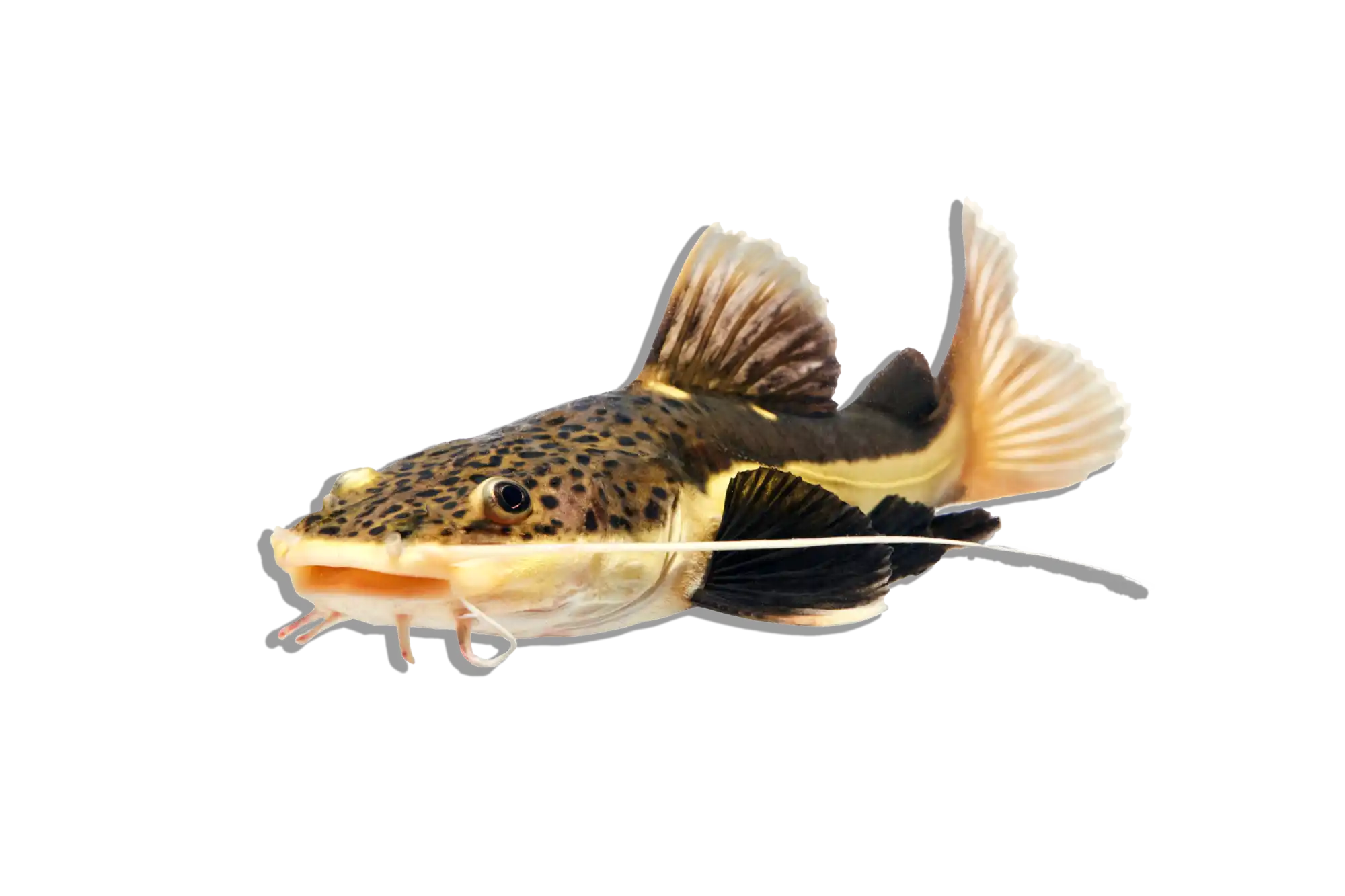
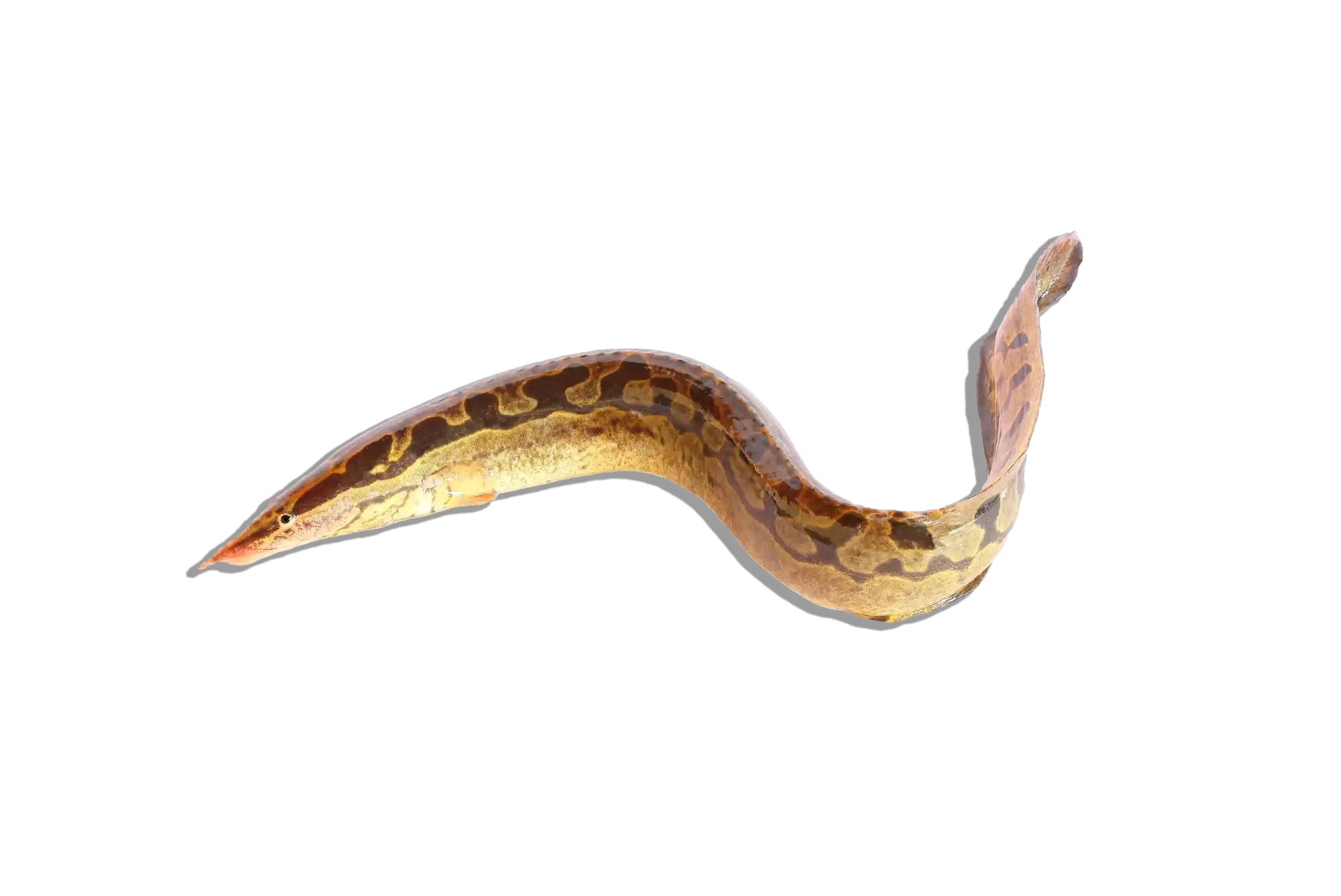
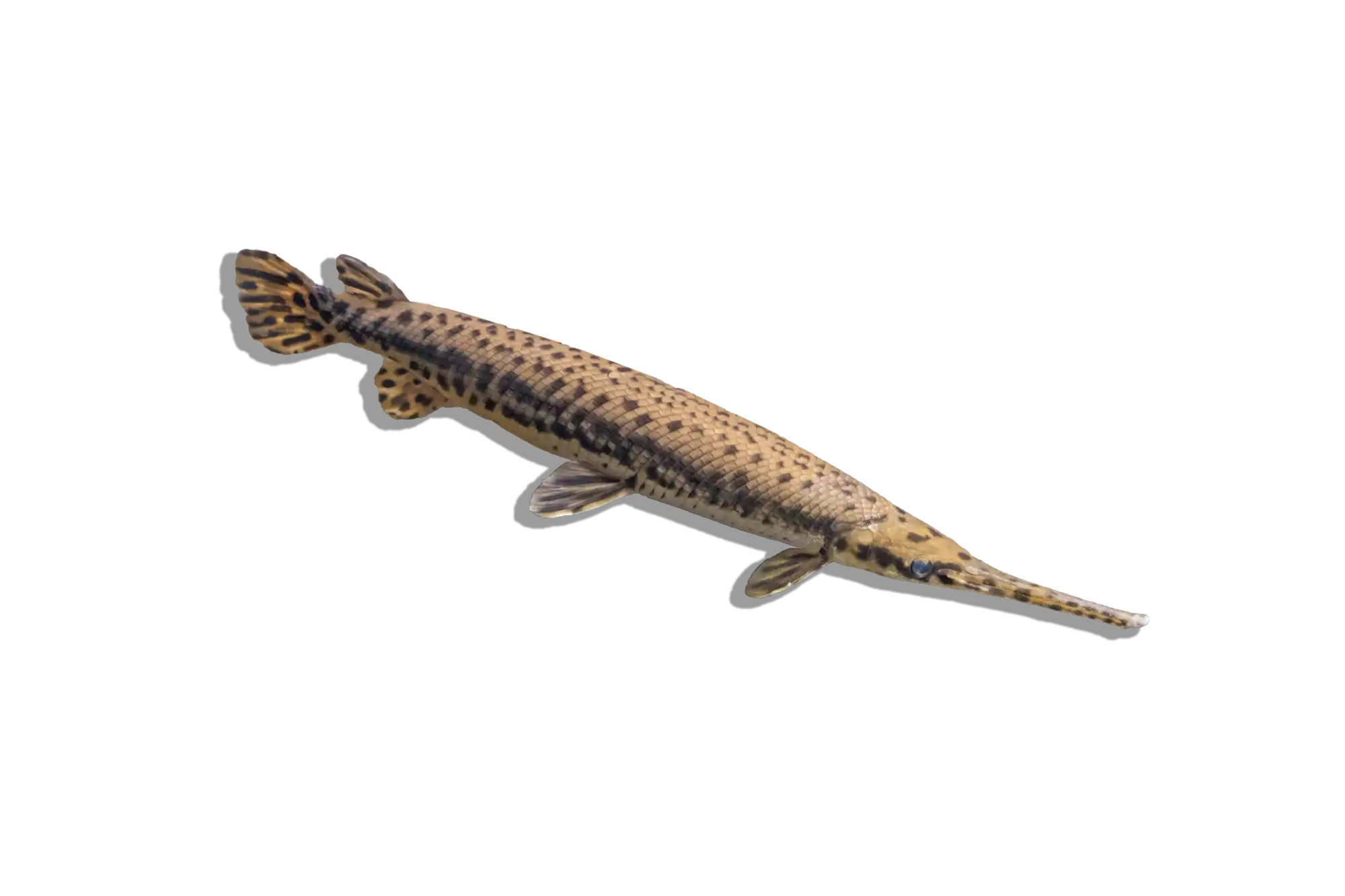
Common Name: Leopard Bush Fish
Scientific Name: Ctenopoma acutirostre
Other Names: Leopard Ctenopoma, Spotted Climbing Perch
The Leopard Bush Fish is a striking predatory species known for its intricate leopard-like spotted pattern and ambush hunting style. This labyrinth fish belongs to the Ctenopoma family, which is related to the popular gouramis. Unlike many fast-moving predators, this species relies on stealth, using its excellent camouflage to blend into aquatic plants and driftwood before striking unsuspecting prey. Its hardy nature and unique behavior make it an excellent choice for aquarists interested in an exotic freshwater predator.
Habitat and Distribution:
Native to Central Africa, Ctenopoma acutirostre is widely found in the Congo River Basin, including its slow-moving tributaries, floodplains, and densely vegetated swampy waters. These environments are typically warm, slightly acidic to neutral, and rich in submerged vegetation and driftwood, providing ample hiding places for this ambush predator.
Size and Lifespan:
This species grows to about 6-8 inches (15-20 cm) in captivity, with wild specimens sometimes reaching slightly larger sizes. With proper care, it can live for 10-15 years.
Diet and Behavior:
The Leopard Bush Fish is a carnivorous ambush predator. In the wild, it preys on small fish, insects, and crustaceans. In captivity, it should be fed a diet of high-quality carnivore pellets, frozen or live foods such as bloodworms, blackworms, feeder guppies, and small crustaceans. It may refuse dry foods initially but can often be trained to accept them over time. This species is slow-moving and primarily nocturnal, spending most of the day hidden among plants and decorations before becoming active in the evening.
Breeding and Reproduction:
Breeding Ctenopoma acutirostre in captivity is rare but possible. As a bubble-nesting species, the male constructs a floating nest where the female deposits eggs. The male guards the nest until the fry hatch, after which parental care ceases. To encourage breeding, a separate breeding tank with floating plants, warm soft water, and live food conditioning is recommended.
Aquarium Care and Tank Requirements:
A minimum of 55 gallons is required for a single specimen, with a larger tank (75+ gallons) preferred for community setups. Their ideal tank setup includes a soft sand or fine gravel substrate, dense plant coverage with driftwood and caves for hiding, moderate filtration with gentle water movement, dim or subdued lighting to mimic their natural environment, and a secure lid as they are capable jumpers.
Ideal Tank Mates:
Leopard Bush Fish can coexist with peaceful or semi-aggressive species that are too large to be eaten. Suitable tank mates include Severums, Angelfish, Larger Gouramis, Bichirs, Clown Loaches, and other medium to large South American or African cichlids. Avoid small fish like Tetras, Rasboras, or Guppies, as they will likely be eaten.
Difficulty Level:
Intermediate. They require a meaty diet, a well-structured tank with hiding spaces, and tank mates that won’t be mistaken for food.
Water Parameters:
- Temperature: 75-82°F (24-28°C)
- pH: 6.0-7.5
- General Hardness (GH): 4-12 dGH
- Carbonate Hardness (KH): 3-8 dKH
- Ammonia: 0 ppm
- Nitrite: 0 ppm
- Nitrate: <20 ppm (regular water changes required)
Additional Information:
- They are intelligent fish and can recognize their owners over time.
- They may take time to adjust to aquarium life but thrive in a well-planted, dimly lit tank.
- A tight-fitting lid is essential, as they have a labyrinth organ and may attempt to jump.
The Leopard Bush Fish is a fascinating species that combines beautiful patterning with a unique hunting style. With proper care and a suitable environment, they make an excellent choice for aquarists looking to keep a peaceful but predatory fish.