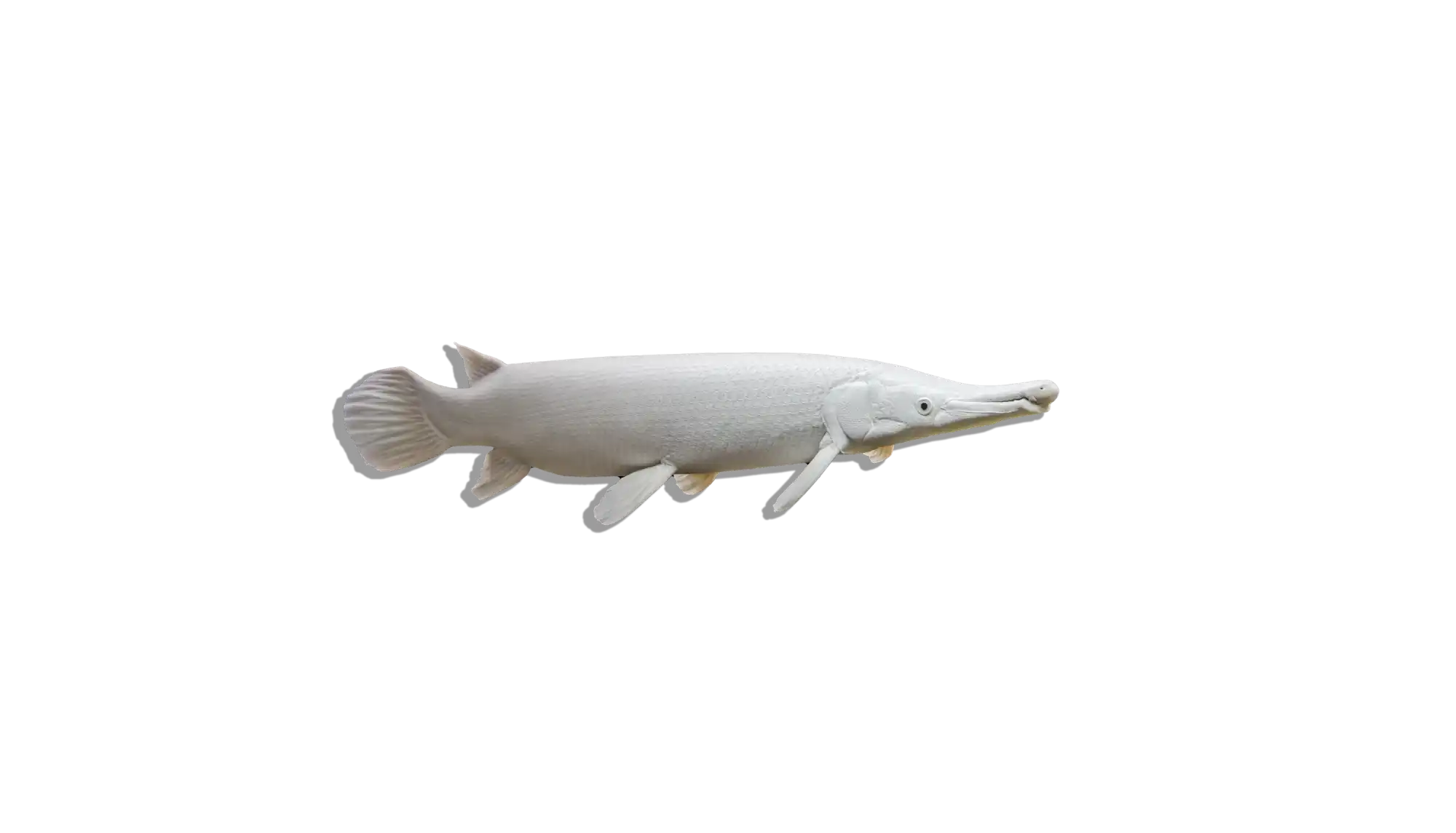
Description
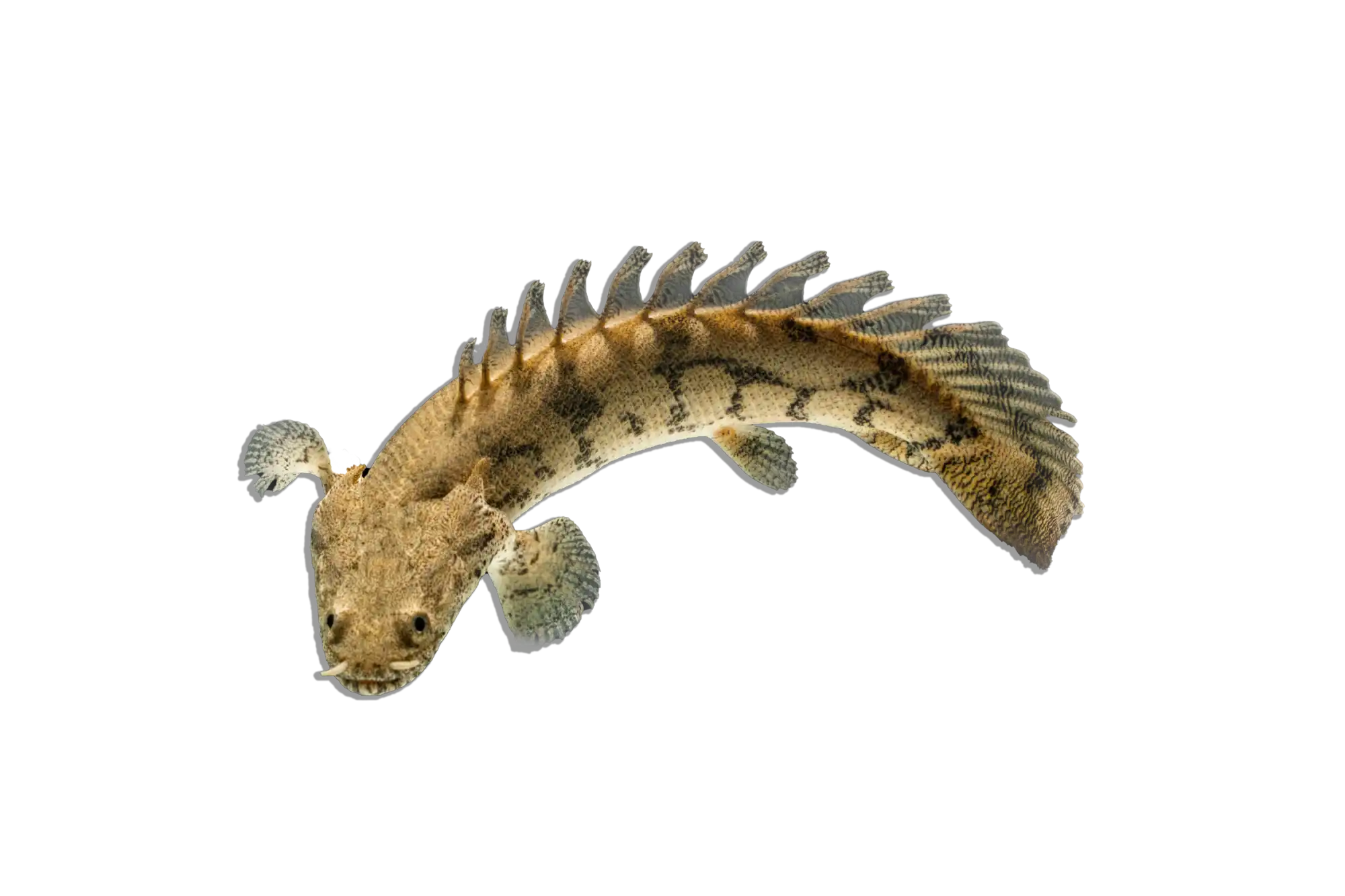
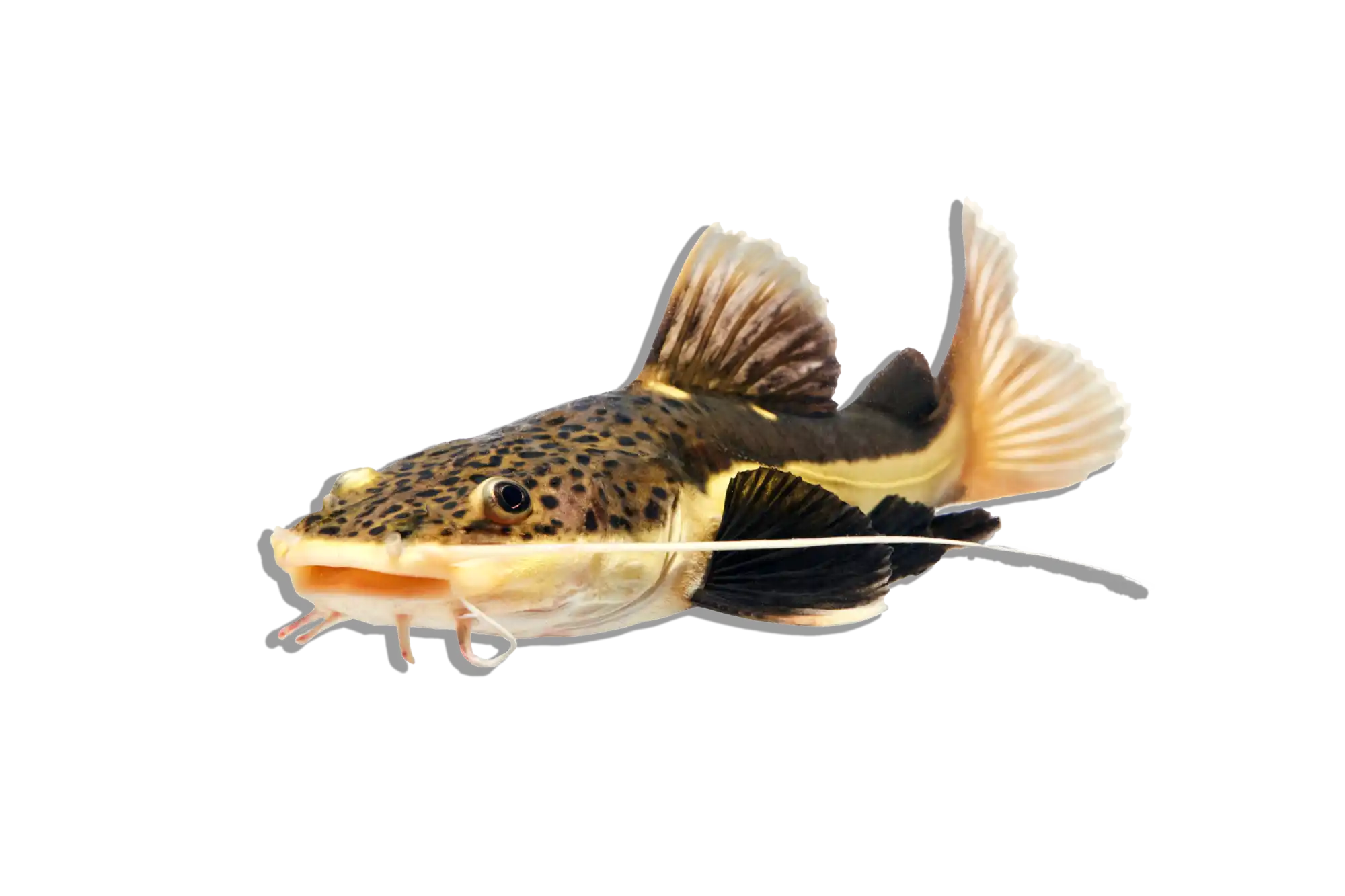
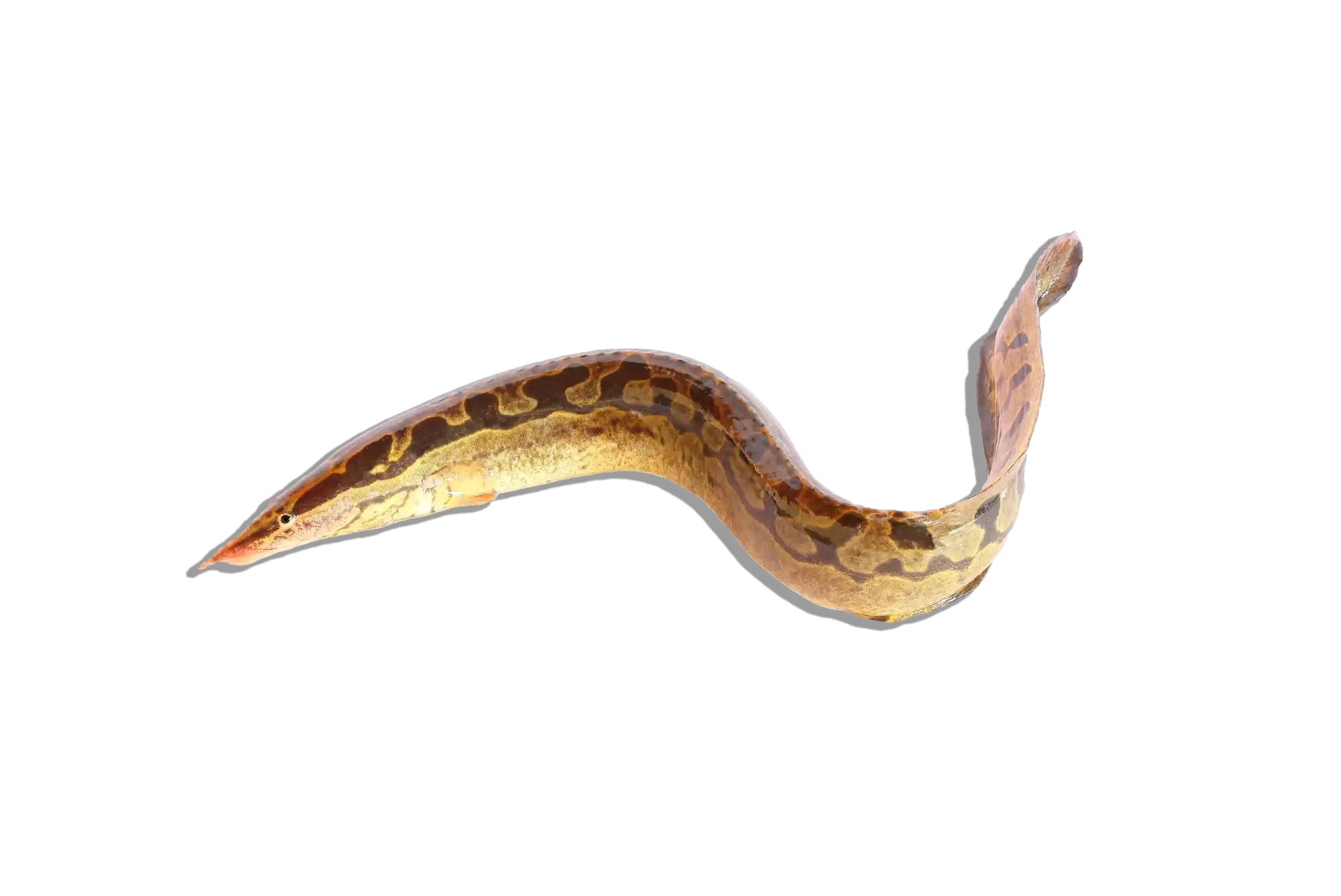
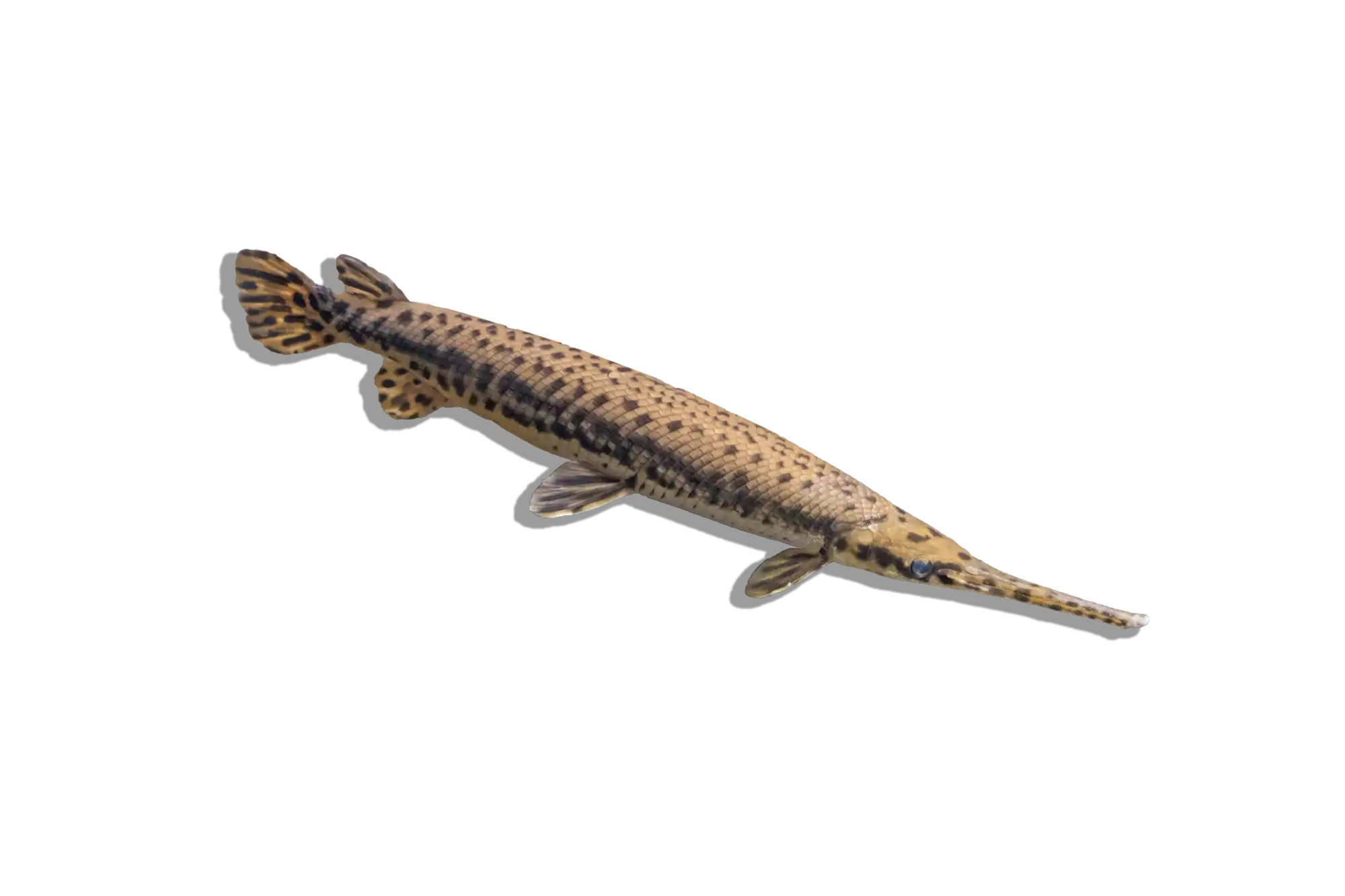
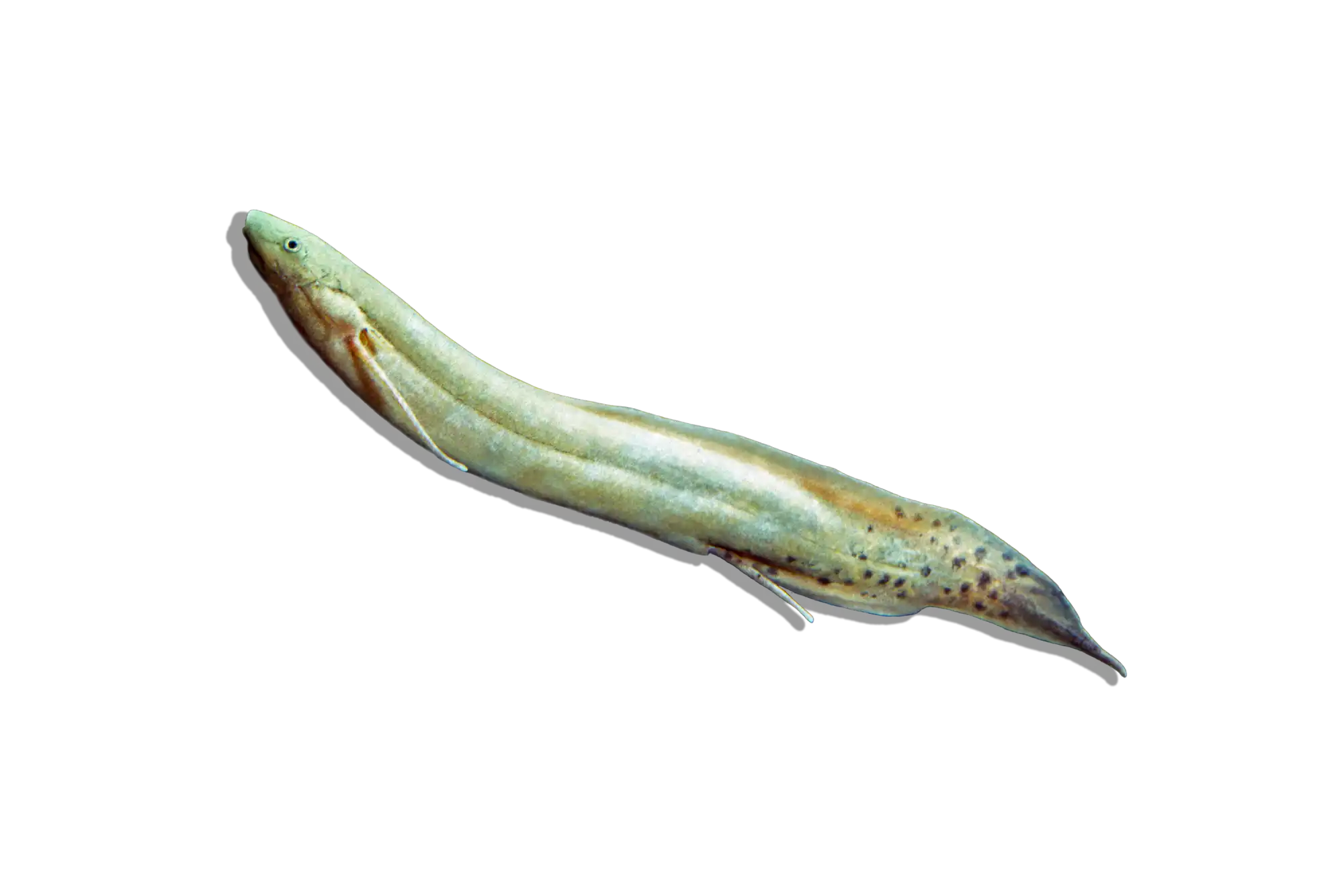
Common Name: Flatnose Catfish
Scientific Name: Anaspidoglanis macrostomus
Other Names: African Flatnose Catfish, Bigmouth Catfish
The Flatnose Catfish is a large, nocturnal species known for its broad, flattened head and wide mouth, which it uses to scavenge along the bottom of rivers and lakes. It has a robust, elongated body with a brownish to gray coloration, often displaying subtle mottling or faint patterns. Like other members of the Claroteidae family, it is well adapted to life in slow-moving waters, using its long barbels to detect food in murky conditions. While it is relatively peaceful, its large size and predatory nature mean that tank mates should be chosen carefully.
Habitat and Distribution:
Native to West and Central Africa, the Flatnose Catfish inhabits slow-moving rivers, floodplains, and lakes with soft, sandy, or muddy bottoms. It prefers areas with submerged logs and dense vegetation where it can hide during the day. It is a nocturnal feeder, actively scavenging and hunting for food at night.
Size and Lifespan:
This species can grow up to 24 inches (60 cm) in length, though most captive specimens remain slightly smaller. With proper care, it can live for 10-15 years.
Diet and Behavior:
The Flatnose Catfish is an opportunistic omnivore, feeding on small fish, crustaceans, insect larvae, and organic matter in the wild. In captivity, their diet should include high-quality sinking carnivore pellets, frozen or live foods such as bloodworms, chopped raw tilapia, earthworms, and occasional plant-based foods like blanched vegetables. They are nocturnal and prefer to hide during the day, becoming more active at night when they forage for food. They are generally peaceful but will eat any tank mates small enough to fit in their mouths.
Breeding and Reproduction:
Breeding the Flatnose Catfish in captivity is extremely rare and largely undocumented. In the wild, they spawn in deep, slow-moving waters, where eggs are laid in protected areas such as submerged roots or caves. Due to their secretive nature and specific environmental needs, successful captive breeding is highly unlikely.
Aquarium Care and Tank Requirements:
A minimum of 180 gallons is required for a single adult, with larger tanks (250+ gallons) preferred for multiple specimens. Their ideal tank setup includes a soft sand or fine gravel substrate to prevent barbel damage, plenty of caves, driftwood, and hiding spaces, powerful filtration to handle their bioload, moderate water movement to replicate their natural habitat, and dim lighting to accommodate their nocturnal lifestyle.
Ideal Tank Mates:
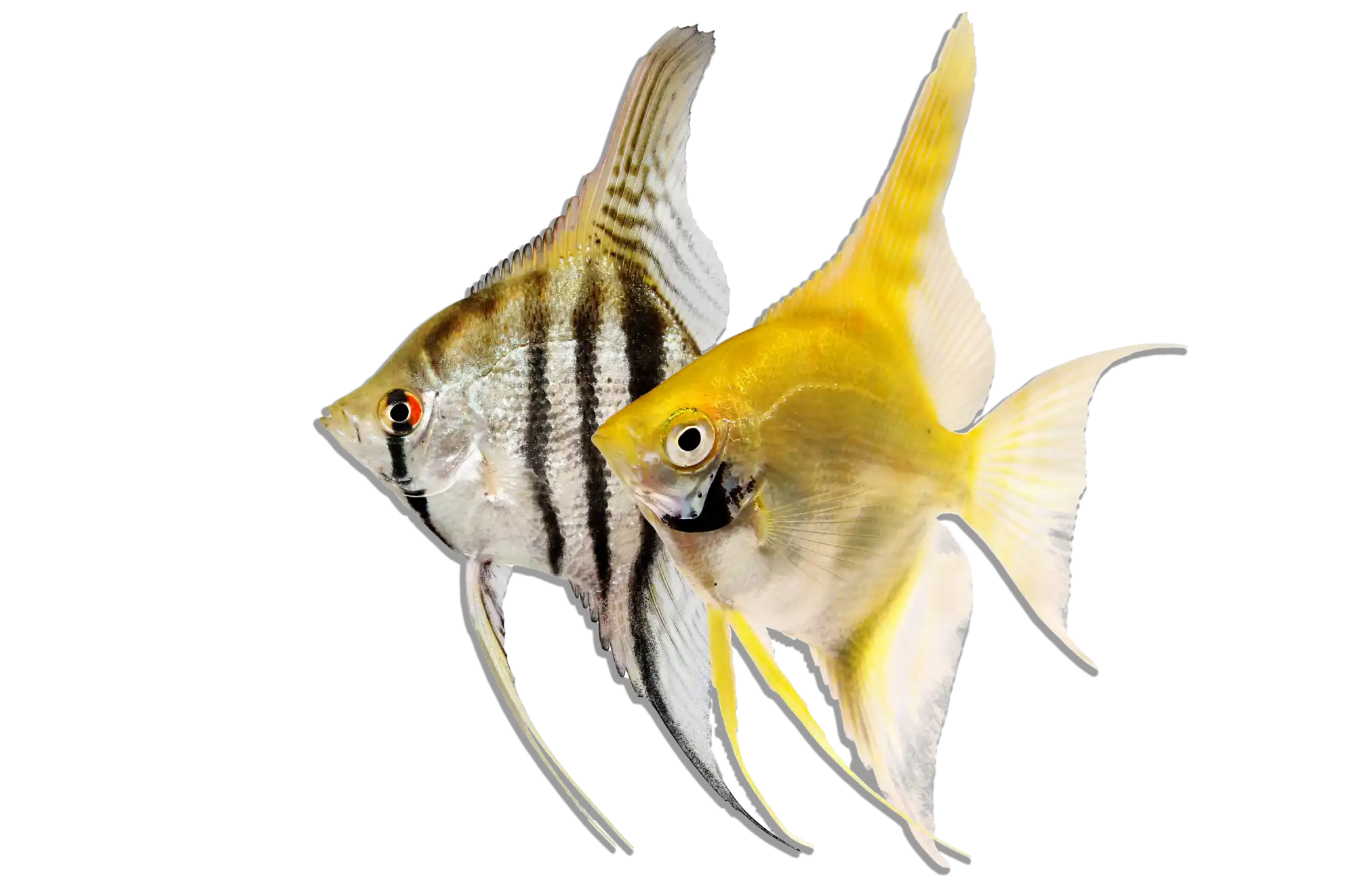
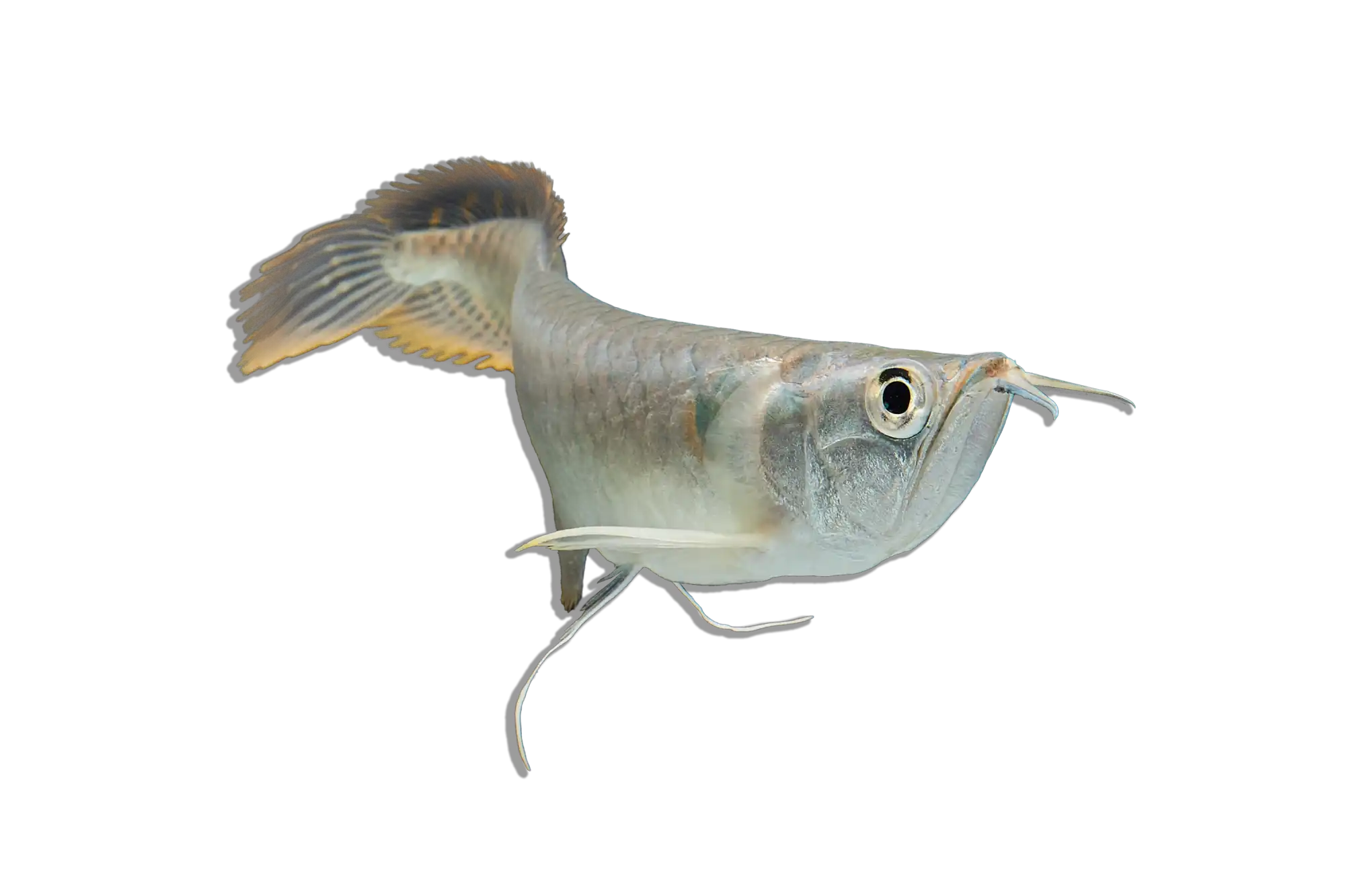
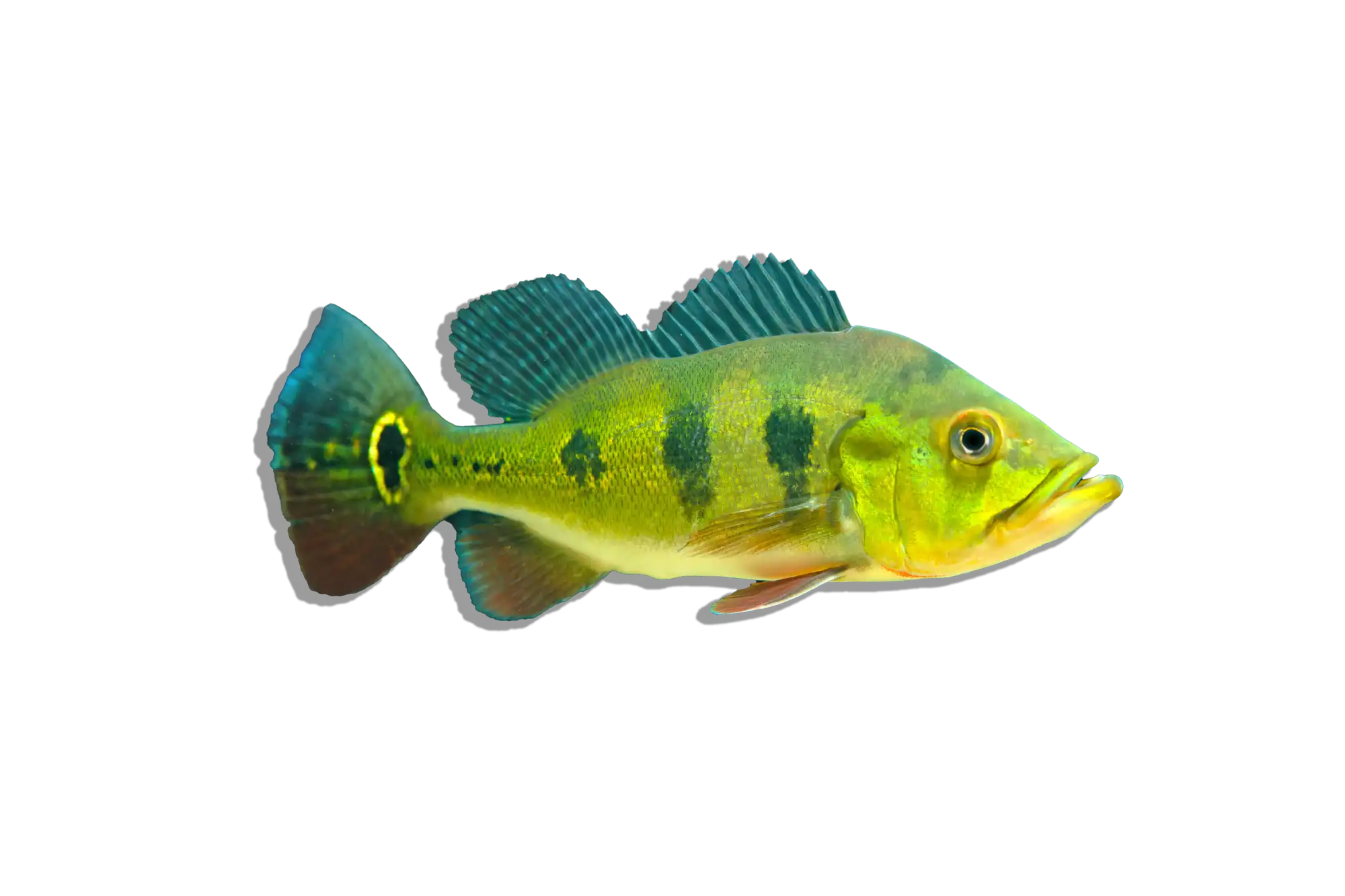
Flatnose Catfish are generally peaceful but require tank mates that are too large to be eaten. Suitable companions include Bichirs, Arowanas, Datnoids, Peacock Bass, Large Synodontis species, and other robust catfish. Avoid small fish, as they will likely be consumed, and highly aggressive species that may outcompete them for food.
Difficulty Level:
Intermediate to Advanced. They require a large tank, stable water conditions, and a carefully managed diet.
Water Parameters:
- Temperature: 74-82°F (23-28°C)
- pH: 6.5-7.8
- General Hardness (GH): 5-15 dGH
- Carbonate Hardness (KH): 4-10 dKH
- Ammonia: 0 ppm
- Nitrite: 0 ppm
- Nitrate: <20 ppm (regular water changes required)
Additional Information:
- They have long, sensitive barbels used for detecting food in low-visibility environments.
- Flatnose Catfish prefer to rest in dark, shaded areas during the day and become active at night.
- Due to their large size and potential predatory behavior, they should only be housed with similarly sized tank mates.
The Flatnose Catfish is a fascinating and hardy species, ideal for aquarists with large predator-friendly aquariums. With proper care, they can become an impressive and long-lived centerpiece in a well-maintained setup.